Portfolio
My name is kethsong and I am a pixel artist, creative consultant, and writer. I specialize in video games, especially smaller startups. I am a contributing artist and author on Gates of Survival, a free PBBG (Persistent Browser Based Game).
Friday, January 12, 2018
New Website
I am moving my services over to http://kethsong.com. I will still continue to update this blog with tutorials, though my main focus will be on the new website until further notice.
Thursday, July 20, 2017
Anti-aliasing Tutorial I
This tutorial will help to explain what anti-aliasing is, as well as how to do it yourself.
Anti-aliasing is a technique used to smooth jagged lines, which appear rough due to the screen not having a high enough resolution to display curves properly. This technique is very important in pixel art for making outlines smoother, and can be used not just for pixel art, but for other things you create, such as logos.
Here is an example of an aliased image, or an image with jagged lines that hasn't had anti-aliasing applied yet (note the jagged appearance of the white circle):

Feel free to download these images and follow along. You can clearly see the white circle is not as smooth as it could be due to the curve. To fix this problem, we note the colors that have jagged lines. On the left it's white/blue, and on the right it's white/red. After noting the two colors, we then choose a value that's between the two colors (in this case, brightness, or how white/black a color is, since white is one of the colors).
Select the red side of the circle with the eyedropper tool in MS paint and click "edit colors". A screen will appear that shoes the number values of the color you selected.
On the right you'll see a sliding bar with white at the top and black at the bottom, and your color in the middle. This is the luminosity bar, and it indicates how bright the selected color is. Since white is the other value, and it is at the top of the bar, we want a color that's about halfway between red and white. We can drag the slider up to about halfway between red and white (if we were aliasing between non-white or non-black colors we would use a different method).
Once you've selected the new color (which should look pinkish), place pixels around the circle's edge inside the corners. Zoom out and make sure it looks smooth--add and remove pixels as necessary. Once it's smooth-looking, use the same method we described above to do the other side. Select the blue side with the eyedropper, click "Edit Colors", and drag the slider up about halfway, then place the blue pixels on the left side. Here is the result:

Looks much better, doesn't it? But this is just a basic tutorial. Ideally you'll want to use more than one color to make it look even smoother. But how do you know what shades to use, or where to put them? In the next tutorial I'll cover this, as well as anti-aliasing between different non-white/non-black colors, and finally go over more advanced techniques to make your anti-aliasing more accurate. Until then, take care!
-kethsong
Anti-aliasing is a technique used to smooth jagged lines, which appear rough due to the screen not having a high enough resolution to display curves properly. This technique is very important in pixel art for making outlines smoother, and can be used not just for pixel art, but for other things you create, such as logos.
Here is an example of an aliased image, or an image with jagged lines that hasn't had anti-aliasing applied yet (note the jagged appearance of the white circle):

Feel free to download these images and follow along. You can clearly see the white circle is not as smooth as it could be due to the curve. To fix this problem, we note the colors that have jagged lines. On the left it's white/blue, and on the right it's white/red. After noting the two colors, we then choose a value that's between the two colors (in this case, brightness, or how white/black a color is, since white is one of the colors).
Select the red side of the circle with the eyedropper tool in MS paint and click "edit colors". A screen will appear that shoes the number values of the color you selected.
On the right you'll see a sliding bar with white at the top and black at the bottom, and your color in the middle. This is the luminosity bar, and it indicates how bright the selected color is. Since white is the other value, and it is at the top of the bar, we want a color that's about halfway between red and white. We can drag the slider up to about halfway between red and white (if we were aliasing between non-white or non-black colors we would use a different method).
Once you've selected the new color (which should look pinkish), place pixels around the circle's edge inside the corners. Zoom out and make sure it looks smooth--add and remove pixels as necessary. Once it's smooth-looking, use the same method we described above to do the other side. Select the blue side with the eyedropper, click "Edit Colors", and drag the slider up about halfway, then place the blue pixels on the left side. Here is the result:

Looks much better, doesn't it? But this is just a basic tutorial. Ideally you'll want to use more than one color to make it look even smoother. But how do you know what shades to use, or where to put them? In the next tutorial I'll cover this, as well as anti-aliasing between different non-white/non-black colors, and finally go over more advanced techniques to make your anti-aliasing more accurate. Until then, take care!
-kethsong
Finding Inspiration
Sometimes figuring out what to draw is pretty simple. You might see something in real life that inspires you, or you might find something in a game or movie that you want to recreate. But other times it can be difficult, especially when you're unsure of your abilities or have drawn a lot of things.
It's actually a really good thing to try and draw more complex objects (like animals or plants) because it teaches you how to study these things closer. If you're drawing something and asking yourself why it doesn't look right, chances are that you misjudged the slope of the line or darkly shaded a part that should have been lighter. Closely compare the two and you'll start to see what changes you need to make. It's not a matter of whether you can do it, but a matter of how patient you are to find what went wrong and fix it.
As far as inspiration goes though, sometimes the best way to get inspired is to actually clear your head somehow. Obviously everyone has their own preferences, but for me, taking a drive or playing a game usually helps. Another thing that helps is to get involved with art communities. While looking through art galleries online, you might actually see something that inspires you to recreate it or even put your own spin on an idea you never would have considered before. You can often have discussions with people and get critique on your work so you know what you should improve upon. Just be prepared for the occasional useless comment that doesn't give any insight into anything other than their intelligence.
If you have old video game consoles, or some other way to access old video games, try loading these up and studying the art. On modern screens you can see the pixels more clearly since there isn't as much of a blur. You'll notice dithering, anti-aliasing, and general patterns that are common even between games from different developers. Brick walls and pillars with light breaking through a window to illuminate one side, shadows being created from blackness, and changing colors mimicking water movement and other activity. Often times studying these images and putting what you learn into practice can drastically improve your abilities, especially with constant practice.
Sometimes you can't afford to wait for inspiration, though. There are times when you simply have to draw even when you're not feeling fully up to it. I don't subscribe to the notion that you have to only draw when you're inspired. It definitely helps, but I don't think it's mandatory. Some of the best drawings I've created were done when I had a deadline and knew beforehand what I had to do. You might have off days where you feel like you're not in the zone, but patience will get you through those days.
When you've drawn enough, you should eventually hit milestones where you feel like you've visibly improved. Maybe you learned how to draw better lines, or maybe your shading/texturing techniques have improved. Once you start hitting these milestones, you will get to a point where you don't really need inspiration to keep going--just the will to actually get started. And if you do find yourself with inspiration, act on it quickly, because you don't know when it's going to disappear. I think inspiration can push an artist over the threshold from a decent drawing to something that's truly memorable.
It's actually a really good thing to try and draw more complex objects (like animals or plants) because it teaches you how to study these things closer. If you're drawing something and asking yourself why it doesn't look right, chances are that you misjudged the slope of the line or darkly shaded a part that should have been lighter. Closely compare the two and you'll start to see what changes you need to make. It's not a matter of whether you can do it, but a matter of how patient you are to find what went wrong and fix it.
As far as inspiration goes though, sometimes the best way to get inspired is to actually clear your head somehow. Obviously everyone has their own preferences, but for me, taking a drive or playing a game usually helps. Another thing that helps is to get involved with art communities. While looking through art galleries online, you might actually see something that inspires you to recreate it or even put your own spin on an idea you never would have considered before. You can often have discussions with people and get critique on your work so you know what you should improve upon. Just be prepared for the occasional useless comment that doesn't give any insight into anything other than their intelligence.
If you have old video game consoles, or some other way to access old video games, try loading these up and studying the art. On modern screens you can see the pixels more clearly since there isn't as much of a blur. You'll notice dithering, anti-aliasing, and general patterns that are common even between games from different developers. Brick walls and pillars with light breaking through a window to illuminate one side, shadows being created from blackness, and changing colors mimicking water movement and other activity. Often times studying these images and putting what you learn into practice can drastically improve your abilities, especially with constant practice.
Sometimes you can't afford to wait for inspiration, though. There are times when you simply have to draw even when you're not feeling fully up to it. I don't subscribe to the notion that you have to only draw when you're inspired. It definitely helps, but I don't think it's mandatory. Some of the best drawings I've created were done when I had a deadline and knew beforehand what I had to do. You might have off days where you feel like you're not in the zone, but patience will get you through those days.
When you've drawn enough, you should eventually hit milestones where you feel like you've visibly improved. Maybe you learned how to draw better lines, or maybe your shading/texturing techniques have improved. Once you start hitting these milestones, you will get to a point where you don't really need inspiration to keep going--just the will to actually get started. And if you do find yourself with inspiration, act on it quickly, because you don't know when it's going to disappear. I think inspiration can push an artist over the threshold from a decent drawing to something that's truly memorable.
Friday, July 14, 2017
Isometric Pixel Art Tutorial II - Shading the Cube
In our last tutorial we learned how to draw a basic cube, as well as an alternative method to use if you want your cubes to stack together. What we didn't do is choose a light source and then color the object based on where we want the light source to be coming from.
Find the cube image you drew earlier, or download the image from the previous tutorial. Open the image in MS Paint and zoom in as far as you need to. On this cube we can see three sides: the top side, the left side, and the right side. The first thing we need to do is visualize where the light will be coming from. In this case I'll choose the top left.
Now, pick a color you want to use and click the paint bucket tool. Since the light is coming from the top left, we'll make the top side the brightest. Fill the top side of the cube with the color you selected. The next brightest side will be the left side. With the paint bucket tool still selected, click "Edit colors" at the top of the window. You'll see a selection of colors as well as a sliding selector on the right. Click the black arrow or the bar itself and drag downward to a dimmer shade of the color you selected. Fill the left side of the cube.
Now we'll repeat what we just did. Open the edit colors window. Using the sliding selector, make the color even darker than the one we just used. Fill the right side of the cube, which gets the least amount of light based on where we chose to put the light source. We're almost done!
The interior edges of the cube are black, and this is not consistent with the work we just did to the cube faces. Using the eyedropper tool (which will pick a color you've already used in your drawing), select the brightest side of the cube, which should be the top. Open the edit colors window again. Move the slider up and choose a brighter value. Make sure the color you've picked is brighter than all the others.
Now what we want to do is to color the lines inside the cube, but not the outside edges. This will give the appearance that the light is reflecting off the edges of the cube, and make them look more blended. There are several ways to do this. With the brightest color we just picked, select the pencil tool and draw a dot on the first black pixel (on the line that's going straight up). This will prevent the fill tool from turning the outside edges a different color, since we want them to stay black. Below is an example of where to draw the dot:

Next, choose the fill tool and fill the inside lines of the cube. Any black pixels inside the cube that are not touching the white background should be filled. That's it, you're finished! This is a very basic shape, but it is often the backbone of pixel art, including city buildings and houses. With some small modifications, a cube can be turned into a house, a car, a garden, or with some imagination, pretty much anything you can think of.
Shading is the same whether you're drawing a cube or an animal. You consider the light source's origin, the contours of the shape, and shade the object based on where you believe the shadows would fall. It doesn't have to be completely accurate either, as long as you're generally consistent. You can get a good idea of how to shade an object you're drawing by looking at photography of something similar. Abstract things like monsters will still have muscles, facial features, and textures. You can take elements from what you know is real and apply them to the imaginary. But for now, just remember:
Find the cube image you drew earlier, or download the image from the previous tutorial. Open the image in MS Paint and zoom in as far as you need to. On this cube we can see three sides: the top side, the left side, and the right side. The first thing we need to do is visualize where the light will be coming from. In this case I'll choose the top left.
Now, pick a color you want to use and click the paint bucket tool. Since the light is coming from the top left, we'll make the top side the brightest. Fill the top side of the cube with the color you selected. The next brightest side will be the left side. With the paint bucket tool still selected, click "Edit colors" at the top of the window. You'll see a selection of colors as well as a sliding selector on the right. Click the black arrow or the bar itself and drag downward to a dimmer shade of the color you selected. Fill the left side of the cube.
Now we'll repeat what we just did. Open the edit colors window. Using the sliding selector, make the color even darker than the one we just used. Fill the right side of the cube, which gets the least amount of light based on where we chose to put the light source. We're almost done!
The interior edges of the cube are black, and this is not consistent with the work we just did to the cube faces. Using the eyedropper tool (which will pick a color you've already used in your drawing), select the brightest side of the cube, which should be the top. Open the edit colors window again. Move the slider up and choose a brighter value. Make sure the color you've picked is brighter than all the others.
Now what we want to do is to color the lines inside the cube, but not the outside edges. This will give the appearance that the light is reflecting off the edges of the cube, and make them look more blended. There are several ways to do this. With the brightest color we just picked, select the pencil tool and draw a dot on the first black pixel (on the line that's going straight up). This will prevent the fill tool from turning the outside edges a different color, since we want them to stay black. Below is an example of where to draw the dot:

Next, choose the fill tool and fill the inside lines of the cube. Any black pixels inside the cube that are not touching the white background should be filled. That's it, you're finished! This is a very basic shape, but it is often the backbone of pixel art, including city buildings and houses. With some small modifications, a cube can be turned into a house, a car, a garden, or with some imagination, pretty much anything you can think of.
Shading is the same whether you're drawing a cube or an animal. You consider the light source's origin, the contours of the shape, and shade the object based on where you believe the shadows would fall. It doesn't have to be completely accurate either, as long as you're generally consistent. You can get a good idea of how to shade an object you're drawing by looking at photography of something similar. Abstract things like monsters will still have muscles, facial features, and textures. You can take elements from what you know is real and apply them to the imaginary. But for now, just remember:
- Choose a light source
- Apply brightest color facing the light source
- The further away from the light source a surface is, the dimmer it will be
Keep those steps in mind and you shouldn't have any major problems. Play around with this tutorial and put your light source in different places, as well as using different colors and brightnesses. Before long you'll find a shading style you like. Take care!
-kethsong
Thursday, July 13, 2017
MS Paint Keyboard Shortcuts
This post will detail a list of useful MS Paint shortcuts. I use most of these myself as they're much quicker than using the menu or clicking buttons. This is a great resource to bookmark, especially if you are newer to pixel art.
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| CTRL+Mouse wheel up | Zoom in |
| CTRL+Mouse wheel down | Zoom out |
| CTRL+Z | Undo last action |
| CTRL+Y | Redo last action |
| CTRL+A | Select all (entire image) |
| CTRL+X | Cut selected area |
| CTRL+V | Paste selected area |
| CTRL+C | Copy selected area |
| CTRL+E | Show image properties |
| CTRL+G | Enable/disable gridlines |
| CTRL+R | Enable/disable ruler |
There are other shortcuts as well. I don't use them quite as much but they are still pretty useful:
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| CTRL+N | New image |
| CTRL+O | Open image |
| CTRL+S | Save image |
| CTRL+P | Print image |
| CTRL+I | Invert colors |
Useful keys while drawing:
Holding SHIFT while using tools such as the line tool, rectangle tool, and ellipse tool, will allow you to draw perfect versions of those things. For example, drawing with the rectangle tool while holding shift will let you draw squares. Drawing with the line tool while holding shift will let you draw a straight line in 45 degree increments.
There are other shortcut keys, but for the sake of brevity I've included the ones I think are most useful. There may even be others I don't know about. Feel free to experiment or research additional ones, and let me know in the comments below if you find this guide useful or have feedback. Thank you!
Isometric Pixel Art Tutorial I - Drawing a Cube
In isometric pixel art, most people start learning basic shapes such as cubes. Cubes are fairly easy to draw due to all the edges and faces being the same length. This makes it appear very clean, polished, and consistent. To start out, open up MS Paint (or if you have a different program, feel free to use it, although this particular tutorial assumes you are using Paint).
If you make a mistake at any point in this tutorial, press CTRL+Z. This will undo the last changes you made, and you can do it several times in a row, though there is a limit of how much it will undo.
If you want to see a square-like grid to help you draw and align the pixels, you can turn on gridlines by clicking View and then checking the Gridlines box. Select black, and draw three pixels side by side. If you need to see closer, click View and then zoom in to maximum. You should have something similar to this:

This is your starting point for the cube, and will serve as either the bottom or top corner. Obviously now we need to make the other lines. Choose a side and place two pixels beside each other, making sure you start one block up and one block over from the ends:
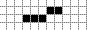
Using the same two-pixel strategy, do this several times more, until you have it as long as you want it to be. Make sure you begin your count from the center of the 3 pixel line at the bottom/top, the reason being that pixel serves as a corner and counts towards either side. So, we now have this:
Now that we've got the bottom of the cube, and our two lines measuring 10 pixels in length, we will draw new lines. These lines will also be 10 pixels long and will extend upwards from three points: the left side, the right side, and the center pixel at the bottom (in the group of three). Remember on this step you're actually drawing nine pixels since you're starting from the first one. That will give us the following result:
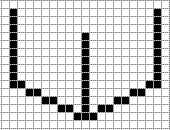
Looks pretty blocky so far, but bear with me. Now that the entire bottom part of the cube is done, all that's left is to draw the remaining lines that will complete the top side of the cube. There are four lines to be drawn, this time starting from either of the three vertical lines we just drew. Remember to count the pixels that are already there when doing your lines! We'll use the same two pixel strategy and connect them, like so:
Now we just have to draw the other two lines. Notice how there's another three-pixel section at the top? When the lines meet, they form this area. Draw the last two 10-pixel lines at the top of the cube to make the completed image:
Finally the shape is done! Still looks really blocky though. Turn off gridlines if you have them on, and zoom out to normal size, and you'll see the result:

So now we've finished a cube. 10 pixels isn't a lot to work with, but for learning purposes it's perfect. And we'll use this completed cube in the next tutorial, which will teach you how to properly shade these shapes, as well as to choose a light source and adjust color values based on where the light is. If you want a bigger one, feel free to experiment and draw bigger shapes, as the shading tutorial will work regardless of what size the cube is. Stay tuned!
-kethsong
Additional Information
If you're wondering why the starting line is three pixels wide rather than two, the answer is simple (the post is done otherwise). With the bottom corner being only two pixels wide, the nearby edge will have to be either on the left or right, rather in the middle. This creates a cube that looks a bit askew, especially as you draw bigger ones. Take a look at this example:

On the left, a starting line of three pixels is used. On the right, a starting line of two pixels is used. The cube on the left is more visually pleasing, but the cube on the right has useful purposes as well. Say you wanted to connect these blocks together, like you would see on Tetris or Minecraft. In this case, it's better to start with a two-pixel line rather than three, because they stack better. Note the following image, with 3-pixel vs 2-pixel cubes:

So basically if you want to build things from the blocks you draw, or you want to connect them together, it's best to start with 2-pixel lines.
If you make a mistake at any point in this tutorial, press CTRL+Z. This will undo the last changes you made, and you can do it several times in a row, though there is a limit of how much it will undo.
If you want to see a square-like grid to help you draw and align the pixels, you can turn on gridlines by clicking View and then checking the Gridlines box. Select black, and draw three pixels side by side. If you need to see closer, click View and then zoom in to maximum. You should have something similar to this:
This is your starting point for the cube, and will serve as either the bottom or top corner. Obviously now we need to make the other lines. Choose a side and place two pixels beside each other, making sure you start one block up and one block over from the ends:
Using the same two-pixel strategy, do this several times more, until you have it as long as you want it to be. Make sure you begin your count from the center of the 3 pixel line at the bottom/top, the reason being that pixel serves as a corner and counts towards either side. So, we now have this:
Now that we've got the bottom of the cube, and our two lines measuring 10 pixels in length, we will draw new lines. These lines will also be 10 pixels long and will extend upwards from three points: the left side, the right side, and the center pixel at the bottom (in the group of three). Remember on this step you're actually drawing nine pixels since you're starting from the first one. That will give us the following result:
Looks pretty blocky so far, but bear with me. Now that the entire bottom part of the cube is done, all that's left is to draw the remaining lines that will complete the top side of the cube. There are four lines to be drawn, this time starting from either of the three vertical lines we just drew. Remember to count the pixels that are already there when doing your lines! We'll use the same two pixel strategy and connect them, like so:
Now we just have to draw the other two lines. Notice how there's another three-pixel section at the top? When the lines meet, they form this area. Draw the last two 10-pixel lines at the top of the cube to make the completed image:
Finally the shape is done! Still looks really blocky though. Turn off gridlines if you have them on, and zoom out to normal size, and you'll see the result:
So now we've finished a cube. 10 pixels isn't a lot to work with, but for learning purposes it's perfect. And we'll use this completed cube in the next tutorial, which will teach you how to properly shade these shapes, as well as to choose a light source and adjust color values based on where the light is. If you want a bigger one, feel free to experiment and draw bigger shapes, as the shading tutorial will work regardless of what size the cube is. Stay tuned!
-kethsong
Additional Information
If you're wondering why the starting line is three pixels wide rather than two, the answer is simple (the post is done otherwise). With the bottom corner being only two pixels wide, the nearby edge will have to be either on the left or right, rather in the middle. This creates a cube that looks a bit askew, especially as you draw bigger ones. Take a look at this example:
On the left, a starting line of three pixels is used. On the right, a starting line of two pixels is used. The cube on the left is more visually pleasing, but the cube on the right has useful purposes as well. Say you wanted to connect these blocks together, like you would see on Tetris or Minecraft. In this case, it's better to start with a two-pixel line rather than three, because they stack better. Note the following image, with 3-pixel vs 2-pixel cubes:
So basically if you want to build things from the blocks you draw, or you want to connect them together, it's best to start with 2-pixel lines.
Wednesday, July 12, 2017
Applying Pixel Dithering
In pixel art, dithering can be utilized in various situations. It can be used to smooth out color transitions, or to create shadowed areas. For example, say we want to make a pixel art sky scene with clouds, and we're limited to two colors, blue and white. Note the following example I've drawn up:
Looks pretty plain--just a couple white blobs in a blue sky. There aren't any shadows under the cloud to accentuate the curves. Without dithering, as well as being limited to two colors, there wouldn't be much else you could do to fix up this image. However, we can use dithering to make the pixel art better, by dithering the bottom of the clouds like so:
Note how the dithering gives the bottom of the clouds a darker appearance by essentially cutting the white in half with a checkerboard pattern. Let's look at another example that uses more colors as well as a detailed background. In the earlier tutorial I used metallic pipes as an example of how you could apply dithering to make it appear cleaner. Look at this section of pipe:

There is no dithering, and the majority of color runs from top to bottom in thin strips, leaving clearly visible lines. Instead, we can use dithering to smooth these transitions, by applying it the other way, like so:

This technique was often vital to video game artists in the past, who had to make do with a limited color palette. By understanding and practicing techniques such as this, you should start to notice details about objects that you hadn't considered before, such as where any light will hit the objects and where their shadow will be cast. Practice makes perfect!
-kethsong
Looks pretty plain--just a couple white blobs in a blue sky. There aren't any shadows under the cloud to accentuate the curves. Without dithering, as well as being limited to two colors, there wouldn't be much else you could do to fix up this image. However, we can use dithering to make the pixel art better, by dithering the bottom of the clouds like so:
Note how the dithering gives the bottom of the clouds a darker appearance by essentially cutting the white in half with a checkerboard pattern. Let's look at another example that uses more colors as well as a detailed background. In the earlier tutorial I used metallic pipes as an example of how you could apply dithering to make it appear cleaner. Look at this section of pipe:

There is no dithering, and the majority of color runs from top to bottom in thin strips, leaving clearly visible lines. Instead, we can use dithering to smooth these transitions, by applying it the other way, like so:

This technique was often vital to video game artists in the past, who had to make do with a limited color palette. By understanding and practicing techniques such as this, you should start to notice details about objects that you hadn't considered before, such as where any light will hit the objects and where their shadow will be cast. Practice makes perfect!
-kethsong
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)


